Understanding Bed Bugs
What Are Bed Bugs?
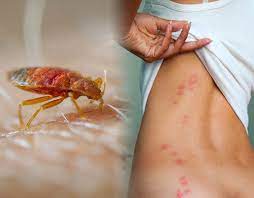
Bed bugs (Cimex lectularius) are small, reddish-brown insects that feed on the blood of humans and animals. They are nocturnal and prefer to hide in cracks and crevices during the day, making them difficult to detect. Bed bugs are notorious for their ability to infest homes, hotels, and other places where people sleep.
Identification of Bed Bugs
- Size: Adult bed bugs are about 5-7 mm long, roughly the size of an apple seed.
- Color: They are flat, oval-shaped, and reddish-brown. After feeding, their bodies swell and become brighter red.
- Eggs: Bed bug eggs are white, about 1 mm long, and are often found in clusters. They are typically laid in hidden areas, such as mattress seams or furniture cracks.
- Nymphs: Bed bug nymphs are smaller and lighter in color. They go through five developmental stages, molting after each stage.
- Bite Marks: Bed bug bites appear as red, itchy welts, often in a line or cluster. They are commonly found on exposed skin areas, such as the arms, neck, and face.
Behavior and Habits
- Feeding: Bed bugs are nocturnal and feed primarily at night. They are attracted to the warmth and carbon dioxide emitted by sleeping humans.
- Hiding Places: During the day, bed bugs hide in small crevices, including mattress seams, bed frames, headboards, and behind baseboards.
- Survival: Bed bugs can survive for several months without feeding, making them resilient and challenging to eradicate.
- Travel: Bed bugs can hitchhike on luggage, clothing, and furniture, making it easy for them to spread from one location to another.

Signs of Bed Bug Infestation
- Bite Marks: Red, itchy bites in a linear or clustered pattern, often on exposed skin.
- Blood Stains: Small blood stains or smears on sheets and pillowcases from crushed bed bugs.
- Fecal Spots: Dark or rusty spots of bed bug excrement on mattresses, bedding, and walls.
- Shed Skins: Bed bugs shed their exoskeletons as they grow, leaving behind translucent skins.
- Musty Odor: A strong, musty odor, often described as smelling like coriander, can indicate a large infestation.
Treatment Methods for Bed Bugs
1. Non-Chemical Treatments
Heat Treatment
- Process: Exposing infested areas to high temperatures (above 45°C or 113°F) to kill bed bugs and their eggs.
- Methods: Professional heat treatments use specialized equipment to heat entire rooms or structures. Alternatively, smaller items can be treated using portable heat chambers.
- Benefits: Effective for entire-room treatments and is eco-friendly as it doesn’t involve chemicals.
Cold Treatment
- Process: Exposing bed bugs to extreme cold (below -18°C or 0°F) for at least 72 hours to kill them.
- Methods: Infested items can be placed in a freezer or treated with specialized cold treatment equipment.
- Benefits: Useful for small items and furniture; chemical-free.
Steam Treatment
- Process: Using steamers that produce temperatures above 100°C (212°F) to treat infested areas.
- Application: Steam is applied directly to infested areas, such as mattresses, furniture, and baseboards.
- Benefits: Effective at killing bed bugs on contact and reaching into small cracks and crevices.

2. Chemical Treatments
Insecticide Sprays
- Types: Various insecticides are available, including pyrethroids, neonicotinoids, and desiccants.
- Application: Sprays are applied to infested areas, including mattresses, bed frames, and furniture.
- Effectiveness: Sprays can kill bed bugs on contact, but some populations have developed resistance to certain chemicals.
Dust Insecticides
- Types: Silica gel and diatomaceous earth are common dust insecticides used against bed bugs.
- Application: Dust is applied to cracks, crevices, and other hiding places where bed bugs reside.
- Effectiveness: Dust works by damaging the bed bugs’ exoskeleton, leading to dehydration and death.
Bed Bug Bombs (Foggers)
- Process: Foggers release a mist of insecticide into the air that settles on surfaces.
- Effectiveness: Limited effectiveness as they often fail to penetrate deep hiding spots, and bed bugs can avoid treated areas.
3. Professional Pest Control
Integrated Pest Management (IPM)
- Approach: IPM combines various control methods, including chemical and non-chemical treatments, with continuous monitoring.
- Steps:
- Inspection: Thorough inspection of the premises to identify bed bug hiding spots.
- Treatment: Use of heat, steam, insecticides, or a combination of methods to eliminate bed bugs.
- Monitoring: Follow-up inspections and use of bed bug traps to ensure complete eradication.
- Education: Educating the occupants on prevention and early detection.
Fumigation
- Process: The entire structure is sealed, and a gas fumigant is released to kill bed bugs.
- Effectiveness: Highly effective for severe infestations but requires the building to be vacated during treatment.

Preventive Measures
1. Regular Inspection
- Frequency: Inspect your bed and surrounding areas regularly, especially if you have recently traveled or brought in used furniture.
- Tools: Use a flashlight to check seams, crevices, and hidden areas for signs of bed bugs.
2. Protective Covers
- Mattress Encasements: Use bed bug-proof mattress encasements to prevent bed bugs from infesting your mattress and box spring.
- Benefits: Makes it easier to spot and remove bed bugs and protects your bedding.
3. Clutter Reduction
- Organize and Declutter: Reduce clutter in your home, particularly in bedrooms, to minimize bed bug hiding places.
- Storage: Store items in sealed plastic containers rather than cardboard boxes.
4. Safe Travel Practices
- Hotel Inspections: Inspect hotel rooms for signs of bed bugs before settling in. Check the mattress, headboard, and surrounding furniture.
- Luggage Management: Keep luggage off the bed and on a luggage rack. Upon returning home, inspect and vacuum your luggage, and wash clothes in hot water.
5. Used Furniture Precautions
- Inspection: Carefully inspect used furniture before bringing it into your home.
- Treatment: Consider treating used furniture with heat or steam before use.

Dealing with Bed Bug Infestations
1. Early Detection and Response
- Importance: Early detection is crucial in preventing a small bed bug problem from becoming a full-blown infestation.
- Actions: If you suspect a bed bug infestation, take immediate action by cleaning, treating, and contacting a professional if needed.
2. Cleaning and Laundry
- Process: Wash all bedding, linens, curtains, and clothing in hot water and dry on the highest setting. Items that cannot be washed should be placed in a dryer on high heat.
- Vacuuming: Thoroughly vacuum the entire area, including mattresses, bed frames, carpets, and furniture. Dispose of the vacuum bag or clean the vacuum canister immediately.
3. Bed Bug Traps and Monitors
- Types: Interceptor traps can be placed under bed legs to catch bed bugs as they attempt to climb onto the bed.
- Monitoring: Use traps to monitor bed bug activity after treatment and ensure they do not return.
4. Professional Help
- When to Call a Professional: If the infestation is widespread or resistant to DIY treatments, professional pest control services should be contacted.
- Selecting a Pest Control Company: Choose a licensed and experienced pest control company that uses a combination of treatment methods and follows IPM principles.

Conclusion
Bed bugs are resilient pests that require a comprehensive approach to control and eliminate. Regular inspection, preventive measures, and prompt treatment are essential in managing bed bug infestations. If a bed bug problem persists or is severe, professional pest control services should be sought to ensure complete eradication. By understanding the behavior of bed bugs and implementing effective treatment strategies, you can protect your home and prevent future infestations.
